Simplified balance sheet. The procedure for filling out the balance sheet and financial performance report
- Purpose of the article: displaying information about availability Money as part of the company's additional fund. Exception: revaluation of a company's non-current assets.
- Line in the balance sheet: 1350.
- Account numbers included in the line: account credit balance.
On line 1350 balance sheet information about the amount of additional capital of the organization is displayed. According to the current legislation, the main sources of its formation are identified:
- procedure for revaluation of non-current assets - increasing their initial value when bringing the value of property to market prices, for example, to attract additional financing for activities;
- positive difference between nominal value own valuable papers joint-stock companies and the price of their sale to shareholders - the share premium of the organization.
Note from the author! According to federal law about joint stock companies, minimum size the authorized capital of public companies is 100 thousand rubles; for non-public companies the minimum threshold is 10 thousand rubles. Any change in the size of the authorized capital is considered only after full payment of the initial amount.
In addition to joint stock companies, share premiums may arise from limited liability companies in cases where the shares of the founders are sold at a higher nominal value.
- Acceptance of targeted financing funds into the company's accounting records, the receipt of which is aimed, for example, at the purchase of fixed assets necessary for the successful functioning of the company, etc.
- positive exchange rate differences that may arise during the revaluation of assets and sources of their formation, expressed in foreign currency for the operation of the company abroad, in Russian rubles.
- positive exchange rate differences that may arise during the formation of the authorized capital of a company, when the founders or shareholders of the organization contribute their share in foreign currency and the exchange rate on the date of official registration of the size of the authorized capital is lower than the exchange rate on the day of the actual contribution of funds by the founder of the company;
- additional contributions of the founders of limited liability companies to the property of the company without changing the initially established size of the authorized capital.
Line 1350 of the balance sheet belongs to the section Capital and reserves of the passive part of the balance sheet: information on credit 83 of the account should be reflected here - the amount of additional capital formed at the enterprise as of December 31 of the current year, the previous one and the one preceding the previous one.
Something to keep in mind! Line 1350 displays the incomplete size of the organization's additional fund. That part of the capital that is formed through the revaluation of the company’s non-current assets is recorded in line 1340 of the balance sheet. In this regard, in-depth monitoring of the sources of fund formation is necessary.
Since this fund is formed as an additional fund, the funds are not used in the main activities of the organization. The formation of additional capital is necessary in the following cases:
- making a decision to increase the authorized capital of the organization using the additional fund;
- repayment of the decrease in the price of non-current assets resulting from the revaluation procedure;
- negative exchange rate differences that may arise when revaluing assets and sources of their formation, expressed in foreign currency for the operation of a company abroad, into Russian rubles;
- negative exchange rate differences that may arise during the formation of the authorized capital of a company, when the founders or shareholders of the organization contribute their share in foreign currency and the exchange rate on the date of official registration of the size of the authorized capital is higher than the exchange rate on the day of the actual contribution of funds by the founder of the company.
Regulatory regulation
The use of account 83 to generate information about the organization’s additional capital funds is carried out in accordance with the Chart of Accounts and other regulatory documents regulating the activities of companies (for example, Federal Law No. 208 of December 26, 1995 for the decision to change the authorized capital of joint-stock companies).
Practical examples of the formation of an additional fund
Example 1
In the public joint-stock company "Yal", in order to attract additional investments, a unanimous decision was made at the meeting of shareholders to increase the size of the company's authorized capital. The new shareholder was sold 50 shares of the company at 12 thousand rubles per share (par value of the shares - 8 thousand rubles per share). Changes in fund size were officially recorded.
Accounting entries on completed business transactions:
400 thousand rubles - the size of the authorized capital of the joint-stock company has been increased.
200 thousand rubles - the amount of share premium is included in the additional fund of the company.
Example 2
As part of the charity event, Solntse LLC transferred funds in the amount of 100 thousand rubles for the purchase of machines for modernizing production.
Business transactions
100 thousand rubles - receipt of targeted financing.
100 thousand rubles - reflects the source of additional funding received.
Common entries for transactions with an additional fund formed in the organization
- Formation of the company's additional fund:
Dt01 Kt83 - due to positive revaluation of non-current assets.
Dt Kt83 - due to share premium arising from a positive difference between the sale price of securities to shareholders and their nominal value. Also, this accounting entry serves as a reflection of positive exchange rate differences on deposits of the company’s founders, which are denominated in foreign currency.
Dt86 Kt83 - at the expense of funds received for targeted financing of the organization’s activities.
- Spending of the company's additional capital:
Dt83 Kt80 - making a decision to increase the authorized capital of the organization at the expense of the company’s own assets, incl. means of additional capital.
Dt83 Kt75 - use of fund funds to pay off emerging obligations when settling accounts with the founders, for example, when reducing the size of the authorized capital. Also, this entry in accounting is a reflection of negative exchange rate differences on contributions from the founders of the company, which are denominated in foreign currency.
Since it is the main type of accounting reporting, it carries a meaning dedicated to financial condition object of business activity. At the same time, a beginner may find its structure incomprehensible and confusing, because in addition to complex page numbering, one also has to deal with the concept of codes, which sometimes becomes a whole problem. This article is devoted to decoding the lines of the balance sheet.
Download the form Balance sheet (form according to OKUD 0710001) possible by .
Simplified form of Balance available at .
Let's look at all the balance line codes by section.
Section 1 - Non-current assets
This section contains information about what low-liquidity assets the company owns. Usually these are equipment, premises, buildings, intangible assets and others.
Section 2 - Current assets
Current assets are the most highly liquid assets of an enterprise. These include goods, accounts receivable, money in cash and accounts, etc.

Section 3 - Capital and reserves

Section 4 - Long-term liabilities

Section 5 - Current Liabilities
Assignment of codes and numbers
Codes for certain lines must be indicated in a certain column. It is worth noting that codes are needed mainly so that statistical authorities can combine information presented in different types of balance sheets into one whole. The codes are mandatory to fill out when the balance sheet being compiled must be transferred to state executive structures with further use of information on them.
In a situation where the balance sheet is prepared for a quarter or other reporting period, in order for it to be considered at internal meetings for the purpose of introducing the state of affairs or analyzing the company’s activities, it is not necessary to fill in the lines of codes, since they do not carry any functions in this case.
Line coding is performed only if this reporting documentation is submitted to government agencies and is not an obligation for the internal preparation of reporting balances. Since financial statements are submitted for review to tax authorities only once a year, then the coding applies only to annual balances.
Comparison with old format codes
Previously, the line code consisted of three digits. At the moment, only those codes that are specified in a special appendix to Order 66 of the Ministry of Finance are being considered. This is app #4 which sets up four digit codes for use.
The encoding of the old form differs from the new one only in that the list of these lines changes, their encoding turns into a four-digit indicator, and the detail of the information provided in the balance sheet changes slightly. The row assignments remain the same.
Updated format strings and codes
It should be noted that the asset has a specialized format based on the liquidity factor of the property that the organization has. The least liquid of it will be located at the very top of the column, since it is this property that remains almost unchanged from the beginning of the organization until its liquidation.
The asset lines in the new balance sheet are: 1100, 1150-1260, 1600.
A liability tends to reflect where the company gets money for its operation. And also what part of these funds is the property of the company, and what part is borrowed and requires repayment. This part of the balance sheet plays an important role, since when compared with the asset, one can accurately say whether the company has the funds to successfully continue its activities, or whether the time will soon come to “wind up shop.”
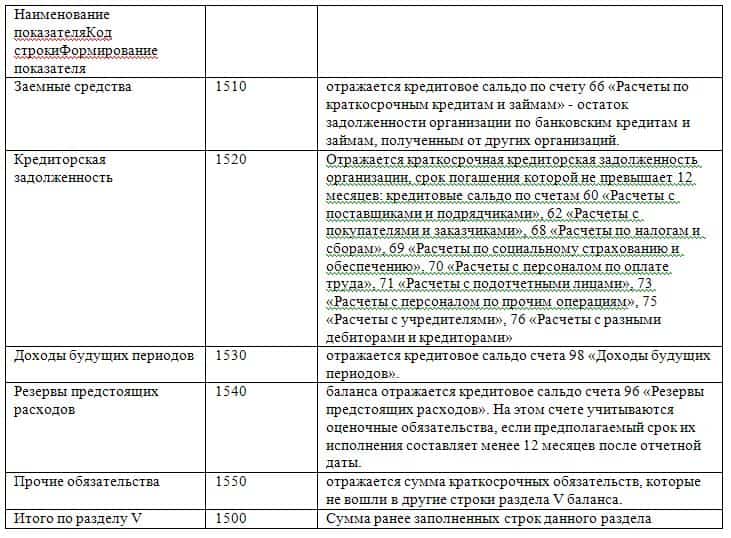
The lines reflecting the passive part of the balance are: 1300, 1360-70, 1410-20, 1500-1550, 1700.
How to decrypt strings
In order to understand how the process of deciphering codes line by line is carried out, it is worth understanding that not a single code is a simple set of numbers. This is a code for a certain type of information.
- The first value confirms the fact that this line relates specifically to the main type of accounting statements, or rather, to the balance sheet, and not to another type of reporting documents.
- The second digit indicates which section of the asset it belongs to. this amount. For example, a unit indicates that the amount belongs to non-current assets.
- The third figure serves as a certain indicator of the liquidity of this resource.
- The fourth digit is initially equal to zero, adopted in order to provide some detailing of the items according to their materiality.
For example, deciphering line 1230 of the balance sheet is accounts receivable.
For a liability, decoding occurs according to the same principle as in the situation with an asset:
- The first digit indicates that it belongs specifically to the balance sheet for the year.
- The second figure demonstrates that this amount belongs to a separate section of the liability column.
- The third number indicates the urgency of the obligation.
- The fourth value is adopted for detailed perception of information.
The total liability is line 1700, which is the sum of line 1300 of the balance sheet, 1400 and 1500.
So, the process of deciphering the codes line by line in the balance sheet occurs on the basis of Appendix No. 4 to 66 Order of the Ministry of Finance. The structure of the codes themselves has a certain meaning. It is important to navigate in itself, or rather, in its sections and articles.
Preparation of a balance sheet is essentially a transfer of account balances accounting in the lines provided for them. Therefore, to correctly draw up a balance sheet, you need not only to keep accounting records correctly and in full, but also to know which accounting accounts are reflected in which line of the balance sheet.
During the consultation, we will provide a breakdown of all the lines of the balance sheet. In this case, we will detail the balance sheet lines according to the most typical accounts, which are reflected on such lines. After all, the procedure for drawing up financial statements in general and the balance sheet in particular, as well as the reflection of certain indicators, is influenced by the characteristics of the organization’s activities and its activities.
By the way, we showed how to draw up a balance sheet in a separate example. And we talked about the content and structure of the balance sheet in another. Let us recall that the current form of the balance sheet presented in tax office and statistical authorities, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n.
Explanation of balance sheet asset lines
| Indicator name | Code | Algorithm for calculating the indicator | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intangible assets | 1110 | 04 “Intangible assets”, 05 “Amortization of intangible assets” | D04 (excluding R&D expenses) - K05 |
| Research and development results | 1120 | 04 | D04 (in terms of R&D expenses) |
| Intangible search assets | 1130 | 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, 05 | D08 - K05 (all regarding intangible exploration assets) |
| Material prospecting assets | 1140 | 08, 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” | D08 - K02 (all regarding material exploration assets) |
| Fixed assets | 01 “Fixed assets”, 02 | D01 - K02 (except for depreciation of fixed assets accounted for in account 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets” | |
| Profitable investments in material assets | 1160 | 03, 02 | D03 - K02 (except for depreciation of fixed assets accounted for on account 01) |
| Financial investments | 1170 | 58 “Financial investments”, 55-3 “Deposit accounts”, 59 “Provisions for impairment of financial investments”, 73-1 “Settlements on loans provided” | D58 - K59 (in terms of long-term financial investments) + D73-1 (in terms of long-term interest-bearing loans) |
| Deferred tax assets | 1180 | 09 “Deferred tax assets” | D09 |
| Other noncurrent assets | 1190 | 07 “Equipment for installation”, 08, 97 “Deferred expenses” | D07 + D08 (except for exploration assets) + D97 (in terms of expenses with a write-off period of more than 12 months after the reporting date) |
| Reserves | 10 “Materials”, 11 “Animals for growing and fattening”, 14 “Reserves for reduction in cost material assets", 15 "Procurement and acquisition of material assets", 16 "Deviation in the cost of material assets", 20 "Main production", 21 "Semi-finished products own production", 23 " Auxiliary production", 28 "Defects in production", 29 "Servicing industries and farms", 41 "Goods", 42 "Trade margin", 43 " Finished products", 44 "Sales expenses", 45 "Goods shipped", 97 | D10 + D11 - K14 + D15 + D16 + D20 + D21 + D23 + D28 + D29 + D41 - K42 + D43 + D44 + D45 + D97 (for expenses with a write-off period of no more than 12 months after the reporting date) | |
| Value added tax on purchased assets | 1220 | 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets” | D19 |
| Accounts receivable | 1230 | 46 “Completed stages of work in progress”, 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, 63 “Reserves for doubtful debts", 68 "Calculations for taxes and fees", 69 "Calculations for social insurance and security", 70 "Settlements with personnel for wages", 71 "Settlements with accountable persons", 73 "Settlements with personnel for other transactions", 75 “Settlements with founders”, 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” | D46 + D60 + D62 - K63 + D68 + D69 + D70 + D71 + D73 (except for interest-bearing loans accounted for in subaccount 73-1) + D75 + D76 (minus VAT calculations reflected in the accounts on advances issued and received) |
| Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents) | 1240 | 58, 55-3, 59, 73-1 | D58 - K59 (in terms of short-term financial investments) + D55-3 + D73-1 (in terms of short-term interest-bearing loans) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 50 “Cash”, 51 “Current accounts”, 52 “Currency accounts”, 55 “Special bank accounts”, 57 “Transfers in transit”, | D50 (except for subaccount 50-3) + D51 + D52 + D55 (except for the balance of subaccount 55-3) + D57 | |
| Other current assets | 1260 | 50-3 " Money documents", 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables" | D50-3 + D94 |
Passive balance: decoding lines
| Indicator name | Code | Which account data is used? | Algorithm for calculating the indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authorized capital (share capital capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners) | 1310 | 80 “Authorized capital” | K80 |
| Own shares purchased from shareholders | 1320 | 81 “Own shares (shares)” | D81 (in parentheses) |
| Revaluation of non-current assets | 1340 | 83 “Additional capital” | K83 (in terms of amounts of additional valuation of non-current assets) |
| Additional capital (without revaluation) | 1350 | 83 | K83 (except for amounts of additional valuation of non-current assets) |
| Reserve capital | 1360 | 82 “Reserve capital” | K82 |
| Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | 99 “Profits and losses”, 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” | Or K99 + K84 Or D99 + D84 (the result is reflected in parentheses) Or K84 - D99 (if the value is negative, it is reflected in parentheses) Or K99 - D84 (same) |
|
| Borrowed funds | 1410 | 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings” | K67 (in terms of debt with a maturity date of more than 12 months at the reporting date) |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 1420 | 77 “Deferred tax liabilities” | K77 |
| Estimated liabilities | 1430 | 96 "Reserves" upcoming expenses» | K96 (in terms of estimated liabilities with a maturity period of more than 12 months after the reporting date) |
| Other obligations | 1450 | 60, 62, 68, 69, 76, 86 “Targeted financing” | K60 + K62 + K68 + K69 + K76 + K86 (all in terms of long-term debt) |
| Borrowed funds | 1510 | 66 “Calculations according to short-term loans and loans", 67 | K66 + K67 (in terms of debt with a maturity of no more than 12 months as of the reporting date) |
| Accounts payable | 60, 62, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76 | K60 + K62 + K68 + K69 + K70 + K71 + K73 + K75 + K76 (in terms of short-term debt, minus VAT calculations reflected in the accounts on advances issued and received) | |
| revenue of the future periods | 1530 | 98 “Deferred income” | K98 |
| Estimated liabilities | 1540 | 96 | K96 (in terms of estimated liabilities with a maturity date of no more than 12 months after the reporting date) |
| Other obligations | 1550 | 86 | K86 (in terms of short-term liabilities) |
To submit an accounting report for 2016, you need to use a new form to submit information about the company’s balance sheet. This article describes how to correctly fill out this form line by line, as well as specific example a fully completed document
09.11.2016Accounting structure for 2016
Accounting reporting documentation for 2016 is transferred by companies to two services at their location:
statistical;
tax
For the current year 2016, the following accounting reports are submitted:
balance sheet;
Report on financial results;
attachments to the two named reports (depending on the situation, these may be reports relating to changes in capital, financial movements, and the intended use of funds).
The legislation also provides that explanations can be added to the accounting records, which are presented in the form of texts or tables. But the auditor's report must be attached without fail. It contains confirmation of the authenticity of all accounting documents. But this is done in the case where the company is subject to audit- Federal Law, Law No. 402, Article 13, paragraph 10.
Non-profit companies also submit accounting reports, the structure of which is as follows:
targeted use of funds;
attachments to mandatory reports.
For individual entrepreneurs, there is no need to submit such accounting reports. For small businesses, it is possible to submit accounting reports in a simplified version. Here are its main nuances:
The balance sheet immediately includes reporting data on financial performance, but without detail.
Applications contain only the information that is needed for evaluation. financial situation of a given company or to assess its financial performance.
If there is no information to complete the above applications, only the required forms are filled out - a balance sheet and financial results report. These rules are confirmed by the following official documents:
order No. 66n (clause 6);
letter No. 03-02-07/1-80 of the Ministry of Finance of our state;
information No. PZ-3/2010 of the Ministry of Finance (clause 17).
When should the balance sheet for the current year 2016 be submitted?
Accounting statements for the annual period are submitted by firms to the local tax service within 3 months from the end of the reporting period, that is, a year - tax code, article No. 23 (clause 1, subclause 5). This report is submitted to the statistical service within the same time frame - Federal Law, Law No. 402, Article 18 (clause 2).
A reporting document containing information about the company’s balance sheet for 2016 is submitted to the relevant departments of local services by March 31 of the following year (in our case, 2017). Interim accounting reports, which are prepared by the company for the convenience of accounting, do not need to be submitted to the tax and statistical services.
Blank report forms (current for 2016-2017)
Download blank forms for filling out a balance sheet:
Features of the simplified form of financial reporting for the current year 2016
Simplified accounting (financial) reporting includes a Balance Sheet, a Statement of Financial Results and a Report on the Purposeful Use of Funds. The following key dates are used for the 2016 report:
In the simplified form of the balance sheet, two mandatory parts are filled in:
asset - non-current and circulating quantities;
liability - the amount of your capital, borrowed finance, accounts payable.
The final results for these sections are recorded in C1600 and C1700, and their digital values must be equal to each other. The remaining lines also have their own encoding, which is entered in an additional column (this is entered into the report independently). This encoding is assigned according to the digital indicator that has the greatest specific gravity as part of the consolidated indicator - order No. 66n (clause 5).
The consolidated items of the balance sheet according to the simplified tax system for 2016 include:
| 1. Tangible non-current assets (fixed funds + unfinished capital investments in them). | 1. Capital and reserves (authorized capital + additional and reserve capital + retained earnings + uncovered loss + revaluation of fixed assets (intangible assets) + own shares (which were purchased for subsequent cancellation) or shares of the founders). |
| 2. Intangible, financial non-current assets ( intangible assets+ long-term cash, including research results, unfinished investments in intangible assets, research). | 2. Long-term borrowed funds (money received as a result of loans or long-term loans). |
| 3. Inventories (the same item exists in the general version of the balance sheet). | 3. Short-term borrowed funds (money received from short-term loans or credits). |
| 4. Cash and equivalents (the same item exists in the general version of the balance sheet). | 4. Accounts payable (a digital indicator of the amount of short-term debt a company has to creditors). |
| 5. Financial and other current assets (short-term investments + accounts receivable + other assets). | 5. Other obligations (short-term and long-term). |
Features of the general form of the balance sheet for 2016
The specifics of the general form of the balance sheet are presented in Order No. 66n, namely in Appendix No. 1 to it. This form can also be used by small businesses, although a simplified version of this report has been developed for them.
The balance sheet for this form also contains several columns that should reflect indicators for the following dates (for 2016):
Let us now consider all the nuances for each column separately.
No. 1 - the number of the explanation to the balance sheet is indicated (if there is an explanatory note),
No. 3 - additionally added column for line-by-line encoding.
Like the simplified form, the general one has two main parts:
Asset - reflects the size of all assets, both current and non-current.
Passive - reflects the magnitude of one’s own capital+ borrowed funds + accounts payable.
Let's break down the balance sheet by section:
Section No. 1 - non-current assets.
Intangible assets. C1110 prescribes the residual value of intangible assets (in accordance with Order No. 153n of the Ministry of Finance of our state, namely with paragraph No. 3 of PBU 14/2007).
Intangible assets include those that meet the following criteria:
ability to generate economic benefits;
possibility of identification (separation/separation) from other assets;
intended for use over a long period of time (over 12 months);
reliable determination of the initial cost of the object (in fact);
there is no material form available.
Example: if the above conditions coincide, then the object is classified as an intangible type of asset - these are works of science, literature, art, various inventions, secret developments, trademarks, etc. In addition, they can also include business reputation, which may appear when purchasing a company as a property complex (although this may only be part of it).
Experts recommend paying attention to the following nuance: intangible assets cannot include expenses that are associated with the organization of the company itself (legal entity), the quality of the company’s personnel - intellectual and business, qualifications and attitude to work - PBU 14/2007, paragraph 4.
C1120 - results of research and development, which are recorded in account “04” (intangible assets).
C1130 - C1140 - indicators of exploration assets, both tangible and intangible (for companies that are subsoil users, they reflect in these lines the costs used for development natural resources- PBU 24/2011, in accordance with order No. 125n of the Ministry of Finance of our state).
C1150 - basic type products. This line includes an indicator of the residual value of funds of the main type for depreciable objects, and for a non-depreciable object - an indicator of the initial cost. Those assets that are classified as funds of the main type must necessarily comply with PBU 6/01 (clause 4), according to Order No. 26n of the Ministry of Finance. The named objects are necessarily owned by the company or have the right of operational management or management. Funds of the main type also include property that a company receives on the basis of a leasing agreement and is subsequently recorded on the balance sheet of the recipient of this lease. Those objects that fall under mandatory registration as property rights also belong to the main type of funds (as soon as they are taken into account on the company’s balance sheet).
It is worth paying attention to the fact that in this section there is no reflection of expenses for the construction of real estate - the line “Construction in progress”. These expenses are entered in this line C1150 - PBU 4/99 (clause 20), in accordance with Order No. 43n of the Ministry of Finance. Although you can add an additional line to decipher expenses for unfinished construction.
C1160 - information about profitable investments in materiel. These, first of all, include the residual value of property that is rented out (that is, leasing), with subsequent accounting in account “03”. In the case when this property was used in connection with other production needs, and after that it will be rented out, then it is reflected in a separate subaccount of account “01” - the composition of funds of the main type. But the transfer of the cost of funds of the main type into profitable investments and vice versa is not carried out - letter No. GV-6-21/418@ Federal Tax Service (dated 05.19.05).
C1170 - financial investments of a long-term nature (for a period of more than 12 months), short-term ones are reflected in C1240 - this is section No. 2, line “ Current assets" Long-term investments include investments in subsidiaries. Financial investments are taken into account in the amount that was spent to acquire them. At the same time, the cost of their shares, which were purchased from the company’s shareholders for their subsequent resale or cancellation (C1320) + interest-free loans that are issued to the company’s workers, should not be classified as financial investments (C1190 - long-term type, C1230 - short-term type) - PBU 19 /02 (clause 3), in accordance with order No. 126n of the Ministry of Finance (dated 12/10/02).
C1180 - deferred tax assets must be contributed by income tax taxpayers (for the simplified tax system - “-”).
C1190 - indicators for other non-current assets, if they have not yet been included in other lines of section No. 1.
Section No. 2 - current assets.
C1210 is a digital indicator of the cost of inventories of a material nature; its decoding is required in the case when these indicators are included in C1210 (that is, they are significant). To decrypt, you need to add the following lines:
materials/raw materials;
costs of work in progress;
products in finished form, as well as goods for subsequent resale;
shipped goods.
C1220 is a digital indicator of value added tax, which is charged on purchased values. For those who work using the “simplified” method, filling out this line must be agreed with accounting policy companies, namely with the amount of “input” VAT (reflected on account “19”), while such companies cannot be independent VAT payers - Tax Code, Article No. 346.11 (clause 2).
C1230 - short-term receivables are registered, which require repayment within one year.
C1240 - financial investments, other than cash equivalents (loans provided to the company for a period of less than 12 months). When determining the current market value of investments, you must use all available information, including information from foreign trade organizers - letter No. 07-02-18/01 of the Ministry of Finance (dated January 29, 2009). If such a determination of the market value for an object that has already been assessed previously cannot be possible, then the value indicator is recorded based on the last assessment result.
The line “Cash and investments” sums up the digital indicators of the value of cash equivalents (the balance of the subaccount of account “58”) + account balances (accounts “50”, “51”, “52”, “55” and “57”). More information about cash equivalents can be found in the Regulations - PBU 23/2011, which is approved by Order No. 11n of the Ministry of Finance of our state (dated 02/02/11). For example, these are demand deposits that are opened in credit institutions.
C1260 - other current assets that were not included in other lines of this section No. 2.
Section No. 3 - capital and reserves.
C1310 - indicator of the amount of authorized capital:
share capital;
authorized capital;
friendly contributions.
The digital indicator for this line must coincide with the indicator recorded in the constituent documentation of the company.
C1320 - your shares or shares of the founders, previously purchased from the company’s shareholders, but not for sale (those that will subsequently be resold are included in C1260). They must be cancelled, resulting in a reduction in the authorized capital. Therefore, this indicator is written in parentheses, since it has a negative value.
C1340 - shows the revaluation of non-current assets. This is an additional valuation of objects that belong to fixed assets + intangible assets (account “83” - additional capital).
C1350 is a digital indicator of the amount of the additional indicator (it is taken without the revaluation amount from C1340).
C1360 - indicator of the reserve fund balance. Reserves include:
those that were formed at the request of the legislative system of our state;
those created according to constituent documents.
Decoding is not needed only if the listed indicators do not have a significant impact.
C1370 - shows the company’s accumulated profit over all years, which has not been distributed, and also includes an uncovered loss with a negative indicator.
The components of these indicators can be described in additionally added lines (this will be the decoding of financial performance - profit/loss).
Section No. 4 - long-term liabilities.
C1410 - long-term borrowed funds (that is, the repayment period is more than one year).
C1420 - income tax payers record information about deferred tax liabilities (those who work under the simplified tax system put “-”).
S1430 - estimated liabilities are recorded when the company recognizes them when maintaining accounting records - PBU 8/2010 (in accordance with Order No. 167n of the Ministry of Finance). This does not apply to small businesses.
C1450 - other long-term obligations that were not included in this section No. 4.
Section No. 5 - short-term liabilities.
C1510 - debt on borrowed funds short-term (that is, those taken for a period of up to one year). This value should be reflected taking into account interest that must be paid at the end of the reporting period.
C1520 is a digital indicator of the total amount of debt on a short-term loan.
C1530 - information on income for future reporting periods. But this must be provided for in accounting regulations. Let's look at an example: a company receives certain sums of money from the budget or amounts of targeted funding. Such finances are accounted for as deferred income. These are accounts “98” and “86” - PBU 13/200 (paragraphs 9 and 20), in accordance with order No. 92n of the Ministry of Finance of our state.
C1540 is a short-term estimated liability (similar to C1430), that is, filling occurs only when such liabilities are officially recognized in the accounting of the company itself.
C1550 - other short-term obligations that have not yet been included in other lines of section No. 5.
Information table: summary of balance sheet lines (general form)
|
Section number, name |
Line by line encoding |
Control |
|
No. 1 - non-current assets |
Dt04 (without R&D expenses) - Kt05 |
|
|
Dt04 (R&D expenses) |
||
|
Dt08 (expenses for intangible search costs) |
||
|
Dt08 (expenses for material search costs) |
||
|
Dt01 - Kt02 (depreciation of fixed assets) + Dt08 (expenses for construction in progress) |
||
|
Dt03 - Kt02 (depreciation of income-type investments) |
||
|
Dt58 + Dt 55 (sub-account “Deposit accounts”) + Dt73 (sub-account “Settlements on loans provided) - Kt59 (reserve for long-term financial investments) |
||
|
A digital indicator of the value of non-current assets, which are not taken into account in other lines of section No. 1 |
||
|
No. 2 - current assets |
Sum debit balances the following accounts: 10, 11, 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 43, 44, 45 + Dt41-Kt42+Dt15+Dt16 (or Dt15-Kt16)- Kt14+Dt97 (short-term expenses) |
|
|
Dt62+Dt60+Dt68+Dt69+Dt70+Dt71+Dt73 (not counting interest-bearing loans) +Dt75+Dt76-Kt63 |
||
|
Dt58+Dt55 (sub-account “Deposit accounts”) + Dt73 (sub-account “Settlements on loans granted”) - Kt59 (reserve for short-term financial investments) |
||
|
Dt50+Dt51+Dt52+Dt55+Dt57-Dt55 (sub-account “Deposit accounts”) |
||
|
Indicator of the value of current assets that were not included in section No. 2 |
||
|
S1200 (result for section No. 2) |
Sum of lines: C1210 to C1260 |
|
|
S1600 (balance) |
||
|
No. 3 - capital and reserves |
||
|
Kt83 (amounts of additional valuation of fixed assets and intangible assets) |
||
|
Kt83 (without amounts of additional valuation of fixed assets and intangible assets) |
||
|
S1300 (result for section No. 3) |
Sum of lines: from C1310 to C137 (the negative indicator of the result obtained is taken in brackets) |
|
|
No. 4 - long-term obligations |
Kt67 (excludes accrued interest, which at the time of drawing up the report has a maturity of up to one year, they are shown in C1510) |
|
|
Kt96 (only long-term estimated liabilities are taken into account) |
||
|
Long-term debt that was not reflected in other lines of section No. 4 |
||
|
С1400 (result for section No. 4) |
Sum of digital indicators of lines: from C1410 to C1450 |
|
|
No. 5 - short-term liabilities |
Kt66+Kt67 (this takes into account accrued interest with a repayment period of up to one year) |
|
|
Kt60+Kt62+Kt76+Kt68+Kt69+Kt70+Kt71+Kt73+Kt75 (only short-term debt is taken into account) |
||
|
Kt98+Kt86 (for targeted funding from the budget) |
||
|
Kt96 (only short-term estimated liabilities) |
||
|
Amounts of digital indicators of debts for short-term obligations that were not taken into account in other lines of section No. 5 |
||
|
С1500 (result for section No. 5) |
Sum of line indicators: from C1510 to C1550 |
|
|
S1700 (balance) |
S1300+S1400+S1500 |
If all data is entered correctly, the digital indicators of the following lines will be equal: C1600 = C1700. If the result does not match, then there is an error in the balance sheet.
An example of filling out a balance sheet form for the simplified tax system for 2016 (with a sample)
The Nadezhda company was registered as a limited liability company in the current year 2016. At the same time, she works in a “simplified” manner. We know the following data that will be required to complete the balance sheet:
An employee of the accounting department of Nadezhda LLC filled out the balance sheet form for 2016 using two forms - general and simplified.
The following key points will be common in filling out:
full company name;
type of main activity;
organizational and legal form;
type of ownership;
a unit of measurement that is not involved in calculations has been crossed out (in our case, all indicators are measured in thousands of rubles);
location of the company (its exact address);
coding system.
Dash marks are placed in both forms in the last two columns, since the Nadezhda company went through the registration procedure in the current year 2016. Therefore, only column No. 4 needs to be filled in, because the company is a newly created one. Information is recorded here as of December 31 of the reporting year (in our case, 2016).
Additionally, you should add column No. 3, in which the line-by-line encoding is recorded.
C1110 - intangible assets: Dt account “04” minus Kt account “05” = 100 thousand rubles - 3 thousand 340 rubles = 96 thousand 660 rubles (but since all digital indicators must be in the form of an integer, the number “ 97").
C1150 - funds of the main type: Dt account “01” minus Kt account “02” = 600 thousand rubles - 20 thousand 40 rubles = 579 thousand 960 rubles (the figure “580” is entered in the report).
C1170 - financial investments: Dt account “58” = 150 thousand rubles (such an investment will be of a long-term type).
C1100 - summary total: C1110+C1150+C1170=97 thousand rubles+580 thousand rubles+150 thousand rubles = 827 thousand rubles.
Entering data on current assets:
C1210 - inventories: Dt account “10” + Dt account “43” = 17 thousand rubles + 90 thousand rubles = 107 thousand rubles.
C1220 - VAT on purchased valuables: Dt account “19” = 6 thousand rubles.
C1250 - cash and equivalents: Dt account “50” + Dt account “51” = 15 thousand rubles + 250 thousand rubles = 265 thousand rubles.
C1200 - summary total: C1210+C1220+C1250=107 thousand rubles + 6 thousand rubles + 265 thousand rubles = 378 thousand rubles.
C1600 - total: C1100 + C1200 = 827 thousand rubles + 378 thousand rubles = 1205 thousand rubles.
All other lines in column No. 4 have “-”.
Now the sequence of filling out liabilities in the balance sheet.
C1310 - authorized capital: Account CT “80” = 50 thousand rubles.
C1360 - reserve capital: Account CT “82” = 10 thousand rubles.
C1370 - retained earnings and uncovered loss: Account CT “84” = 150 thousand rubles (since the indicator has a positive sign, it is not taken into brackets).
C1300 - summary total: C1310+C1360+C1370=50 + 10 + 150 = 210 thousand rubles.
C1520 - short-term accounts payable: Account credit “60” + Account credit “62” + Account credit “70” = 150 + 506 + 89 + 250 = 995 thousand rubles.
C1500 duplicates the C1520 indicator (this is due to the fact that the other lines of this section No. 5 remain unfilled).
C1700 - summary total: C1300+C1500=210+995=1205 thousand rubles.
The remaining passive lines have a “-” because there is no relevant information available.
The results of C1600 and C1700 are equal, this is 1205 thousand rubles. Since the balance in the report is correct, it means that the data was entered without errors.
Column No. 2 was added by the accounting employee himself in order to enter line-by-line coding into it. And column No. 3 contains digital indicators.
C1150 - cost of basic type funds = 580 thousand rubles.
S1170 - financial investments and non-current intangible assets: 97+150= 247 thousand rubles.
C1210 - inventories = 107 thousand rubles.
C1250 - cash and equivalents = 265 thousand rubles.
C1260 - current assets that are not included in other lines = 6 thousand rubles.
С1600 - summary result of the asset division: С1150+С1170+С1210+С1250+С1260.
Now let's look at the liability side of the balance sheet.
C1370 - retained earnings in the line “Capital and reserves”: 50+10+150=210 thousand rubles (calculated according to the indicator that has the largest share in the aggregated indicator).
C1520 - short-term accounts payable = 995 thousand rubles.
The other lines of column No. 3 remain with “-” because the information is missing. In column No. 2 you can also put “-” or enter the encoding corresponding to the indicator.
C1700 - total for liabilities: C1370+C1520.
Since when reconciling the results of the final lines - C1600 and C1700, we get the same number - 1205 thousand rubles, then the balance sheet is filled out correctly.
These forms are signed by a senior employee of the Nadezhda company. After this, the date of signing the documents is indicated.
Svetlana
Is it possible that Simplified accounting is provided on the old forms, Form for KND 0710096, and not on Form for KND 0710099
PBU 4/99, notes 1, 2 in Appendix No. 5 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n). Non-profit organizations that have the right to use simplified accounting methods, including simplified accounting statements (clause 6.1 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n) can generate a Report on the intended use of funds in a simplified form. Line 6100 “Balance of funds at the beginning of the reporting year” of the simplified form of the Report on the targeted use of funds This line provides data on the balance of funds for targeted financing at the beginning of the reporting year (clause 27 of Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia PZ-1/2011). Section “Received funds” of the simplified form of the Report on the targeted use of funds This section provides information on the receipt of funds for targeted financing (clause 27 of the Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia PZ-1/2011).
Procedure for filling out reports
For example, a balance sheet prepared by an enterprise for 2017 should contain data as of December 31, 2017, December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015. The financial results report for the year must contain information on income and expenses that were recognized in the company’s accounting in the reporting and previous year (Read also the article ⇒ Procedure for preparing financial statements). All last year's information is taken from last year's reports.
And for indicators for the current year, information is taken from sources such as:
- The balance sheet for the entire organization for reporting year;
- Indicators of accrued interest on credits (loans) for the reporting year.
If there is no data to fill out any balance line, it is not filled in and a dash is placed. The line code that is indicated in the simplified balance sheet can be found in Appendix 4 to Order of the Ministry of Finance 66n.
An example of filling out a simplified balance sheet for a simplified tax system
In the composition of the received funds, in particular, the following are shown: entrance (share) and membership fees, voluntary contributions from investors, targeted contributions for the acquisition (creation) of non-current assets, financial support for the implementation of targeted programs provided for in the estimate of the NPO, donations in the form of cash and in kind, other income (clause 28 of the Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia PZ-1/2011). In a simplified form of the Report on the targeted use of funds, all received funds for targeted financing are shown with the division: - for contributions and other targeted receipts; — profit from income-generating activities; - other supply.
How to fill out a simplified form of a report on the intended use of funds
Attention
Old “profitable” errors can sometimes be corrected in the current period. If an organization discovers that in one of the previous reporting (tax) periods an error was made when calculating income tax, it can be corrected in the current period only if two conditions are met.< … Сдача СЗВ-М на директора-учредителя: ПФР определился Пенсионный фонд наконец-то поставил точку в спорах о необходимости представлять форму СЗВ-М в отношении руководителя-единственного учредителя. Так вот, на таких лиц нужно сдавать и СЗВ-М, и СЗВ-СТАЖ! < …
When paying for “children’s” sick leave, you will have to be more careful. A certificate of incapacity for caring for a sick child under 7 years of age will be issued for the entire period of illness without any time limits. But be careful: the procedure for paying for “children’s” sick leave remains the same!< …
Balance lines 2017: decoding
When paying the minimum tax, the indicator is indicated on line 280 of section 2.2 of the declaration according to the simplified tax system. · If the organization is on UTII, then the amount of UTII for all quarters is indicated. The indicator is indicated in brackets, no minus sign is used. 2400 “Net profit (loss)” Calculate the value as follows: line 2110 – line 2120 – line 2330 + line 2340 – line 2350 – line 2410 If the result “ Net profit(loss)” will have a minus sign, then it must be written down in the report in brackets; the minus is not indicated. If the resulting value is positive, then there is no need to put it in brackets.
The legislative framework Legislative act Contents Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n dated July 2, 2010 “On the forms of financial statements of an organization” PBU 4/99 “ Financial statements organizations" Rate the quality of the article.
An example of filling out a balance sheet for 2016 in a simplified form
The code of the indicator that has the greatest share or completely forms the indicator of the line “Contributions and other targeted receipts” is determined in accordance with Appendix No. 4 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n. When filling out this line, information about credit turnover for the reporting year on account 86 (analytical accounting accounts) is used: - entrance fees; — membership fees; — targeted contributions; — voluntary contributions; - donations. Line “Contributions and other targeted receipts” = Credit turnover on account 86 (analytical accounts for accounting: entrance, membership, targeted, voluntary contributions and donations) The indicator of the line “Contributions and other targeted receipts” for the same reporting period of the previous year is generally transferred from the Report on the intended use of funds for a given period.
The procedure for filling out the balance sheet in a simplified form. example
Important
For firms engaged in common activities such as trade, transportation or construction, a light version of the form reflects the results financial activities quite complete. Do I need to report to individual entrepreneurs using a simplified form? Not necessarily, but if you wish, you can prepare reports in any form based on the data in the income (and expenses) ledger. Is it possible for NPOs to report in a simplified manner? Yes, instead of a report on financial results, NPOs fill out a simplified report on the use of targeted funds.
The lightweight version is much shorter. You can see how to correctly fill out the balance sheet of an NPO using the simplified tax system in the example (Fig. 1). How to make a simplified balance sheet for the simplified tax system for 2017: form and recommendations First, you need to close the accounting reporting period. To balance the balance, accounts 90, 91 and 99 are closed on December 31 of the reporting year - this is called reformation.
Line code for target funds in a simplified balance sheet
Simplified accounting and reporting are not related to taxation. It can be conducted by companies both using the simplified tax system and other modes, including the general one. This opportunity is provided to small businesses, non-profit organizations (except for foreign agents) and Skolkovo participants.
In the article we will answer the question of whether it is necessary to submit the balance sheet of an LLC under the simplified tax system in 2018, as well as individual entrepreneurs and non-profit organizations. Small businesses, according to Federal Law No. 209 dated July 24, 2007, in 2017 included organizations and individual entrepreneurs with a staff of up to 100 people and revenue excluding VAT of up to 800 million rubles. In this case, the organizational and legal form can be:
On joint stock companies These rules do not apply and they do not have the right to apply simplification in accounting. A individual entrepreneurs it is permitted not to keep accounting records at all and not to submit any financial reports (Article 6 No. 402-FZ).
You can apply immediately explanatory note about the reasons for their occurrence. Enterprises and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified regime are not required to compile it in full. Losses can be explained by writing off overdue accounts receivable and so on.
Tax officials can also clarify your intentions to correct the situation. We remind you that an organization can switch to a simplified system by sending a notification about this to the Tax Office. A sample of filling out a notification about the transition to the simplified tax system from 2018 for individual entrepreneurs, given in the article on our portal, will help you do this.
Dear readers, if you see an error or typo, help us fix it! To do this, highlight the error and press the “Ctrl” and “Enter” keys simultaneously.
