Capital intensity of fixed assets. Capital-labor ratio
For the effective operation of an enterprise, it is important to control the level of income and expenses. This is possible when calculating capital investments made to develop the production cycle.
Expenses for the purchase of equipment are paramount. They form the basis of production means.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FOR FREE!
When making calculations, the capital intensity ratio must be taken into account. It is necessary to assess the rational use of funds that are basic in the production cycle.
The essence of the concept
Capital intensity is a value that is calculated based on the cost of production assets when converting them into the ruble equivalent of finished products. The capital intensity ratio can be calculated using a special formula. The cost of fixed assets (Co) must be divided by the volume of products produced during the activity (P).
The value changes when the company's process optimization decreases or increases. The more efficiently equipment and fixed assets are used, the greater the amount of output that can be obtained. Then the capital intensity indicator may decrease.
As the coefficient increases, it decreases. As a result, the enterprise receives greater profits and economic efficiency of the production process. At the same time, the funds invested in production will be repaid in full.
To calculate capital intensity, the basic formula given above is used. But it has some disadvantages. Among them is the lack of accounting for the depreciation of production assets, which leads to the constancy of their prices. Also, when calculating, all manufactured products are taken into account. However, some part cannot be sold.
According to this formula, it is possible to evaluate the production and technological process, reflecting its dynamics. To assess the production efficiency and payback of goods, you need to use another formula: Fe = ½(Co1+Co2)/Pr. In it, the value of Co1 is taken to be the cost of means of production at the beginning of the billing period, and Co2 - at the end date. Ave. is a value reflecting the quantity of goods sold.
Data for the calculation can be taken from documents reflecting production, price and sales of products for a specific period. It is also important to calculate the restoration amount. It will be needed to increase production output. In this case, you need to focus on the formula Fe = Ss.g./Pg.
In it under Ss.g. refers to the cost of means of production obtained on the basis of average annual calculations. Pg reflects the quantity of products that should be produced within 12 months according to the plan. Each indicator is prescribed in the business plan of the enterprise.
When determining the cost of equipment involved in the technological process, the full value is taken. those on the balance sheet are not taken into account.
Dependence on industries
The capital intensity ratio is required to optimize production processes and evaluate the efficiency of the enterprise. Normative meaning also helps to analyze all industries as a whole. According to such data, the ratio of production assets to gross product is calculated.
Among the types of capital intensity, direct and full are distinguished. When calculating a direct indicator, the degree to which results are obtained by the funds that were involved in the production process when creating products is assessed.
If it is necessary to estimate the total capital intensity, then those funds that were used indirectly in the creation of products are also taken into account. Capital ratio is an important indicator. But it is still considered auxiliary, since paramount importance is given to capital productivity.
Formulas of the main components
When using fixed assets, three important indicators are determined:
- recoil;
- capacity;
- armament.
Capital intensity is based on the number of production assets used to produce products. The size is determined in relation to one ruble of the cost of the product.
Capital productivity shows the amount of output obtained from each ruble invested in fixed assets. On its basis, economic efficiency is determined.
Capital intensity and capital productivity are reciprocal quantities. With efficient and improved use of production means, increased output and reduced capacity are produced.
To calculate capital productivity, the allocation of working machines and equipment that make up the active part of the funds is made. To compare the growth rate and the implementation of the plan, it is necessary to take into account the value of the basics of industrial production per 1 ruble and the cost of equipment for the same amount.
The second indicator is ahead of the first if the share of the active part of fixed assets increases.
Recoil
Capital productivity shows the use of the enterprise's fixed capital in economic and industry assessment. To calculate it, it is important to know the amount of output and the cost of production assets.
The capital productivity indicator determines the volume of production per unit of fixed assets. Based on this indicator, production efficiency is determined. The expression of quantity can be in kind or in money. The calculation is made in general for all funds, as well as for part.
The value is determined at various economic levels:
| Fo | Capital productivity. |
| VP | Product release. |
| Soph | Cost of fixed assets. |
Fixed assets are calculated from the ratio of the average annual cost of capital. But in some cases it is important to take the cost of these funds for the initial and final billing period. Then the funds are added up and divided by 2.
Armament
Capital-labor ratio is an indicator that reflects the efficiency of using a company's production assets. It shows that employees have the means to carry out production.
Among them are:
- tools;
- machines;
- equipment;
- transport;
- buildings;
- buildings, etc.
The balance sheet must be used for the calculation.
Changes in the capital-labor ratio are observed when personnel leave or equipment breaks down. Then the residual value of the funds is taken.
How to calculate the capital ratio
To analyze the efficiency of using funds and the company's activities, certain values can be calculated. The main one is capital intensity. To carry out the calculation, you need to know the balance sheet of the enterprise’s accounting department, taken for a specific period of time. A report showing profits and losses during the period under study is also important.
To calculate, you need to follow a certain sequence:
- You need to determine the cost of fixed assets that have an average annual expression. To do this, you need to add up the cost at the beginning and end of the period, recorded in line 120 of the balance sheet. The result obtained is divided by 2. When planning capital intensity, data from the business plan and program are used.
- Next, the cost of products that were produced over 12 months is calculated. You need to focus on the annual profit and loss report of the enterprise. When planning, you need to refer to the business plan or program.
- Capital intensity is calculated using the formula Fe=Co/B, where the first value is the average annual cost of fixed assets, and B is the cost of products produced over 12 months. The resulting value will be the capital intensity of the enterprise.
- If you need to calculate the capital intensity according to the plan, you need to refer to the business plan. You can also use planned and actual indicators for the past period. An analysis is made based on the data.
Balance overview
The calculation is made on the basis of reporting data on financial indicators and the balance sheet. Income is reflected in the first document, and fixed capital in the second.
The capital intensity will be equal to COR = page 1150 BB (the value of fixed assets by BB)/page. 2110 OFR (reported income).
When calculating the capital intensity of products, you can rely on another formula: COR = page 1150 BB/page. 2200 OFR, where the last value is the company’s profit when selling products based on the financial result.
Condition and usage analysis
Product output can increase and decrease when certain indicators change.
These include:
- availability and use of labor (industrial and production means);
- the company's provision of material resources and their use;
- labor resources used and available.
The analysis must take these factors into account. In this case, the assumption is made that they had equal conditions and acted according to the stipulated plan.
An increase in production volumes occurs with an increase in the amount of fixed assets.
Analysis of fixed assets is carried out on the basis of:
- annual balance sheet report;
- inventory cards;
- invoices for internal movement;
- acts of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets for repair, reconstruction, modernization.
The analysis begins with a study of fixed assets. The relationship between different groups and the total cost is calculated. It is important to increase the UV of active equipment.
- updates;
- disposals;
- growth.
After this, the age of the equipment is determined to determine the nature of the technical condition. Fixed assets are calculated based on depreciation and serviceability coefficients. When comparing indicators for a certain period, one can note the trend of their change.
After this, mechanized, automated, complex automated levels are determined based on the total cost of specific types.
Changes in service indicators are carried out in accordance with the level of mechanization and automation of labor. The number of workers using a specific type of equipment in relation to the total number of employees is taken into account.
Among the indicators of equipment use, there are several types:
After a complete analysis of the work, a generalization is carried out. On its basis, production reserves for fixed assets are determined.
Among them are:
- introduction of equipment that was not previously installed;
- increasing the number of equipment operation changes;
- refusal of equipment downtime outside the plan and within the shift;
- reduction of time losses during equipment operation;
- preparation of organizational and technical measures that will reduce the time spent on equipment operation when producing one unit of product.
Capital intensity must be studied to improve enterprise productivity. To develop measures, it is calculated together with capital productivity and capital-labor ratio.
Attention!
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.
Capital intensity reflects the cost of equipment used per 1 ruble of revenue. The indicator helps to understand whether the company is using its production capacity effectively. An analysis of the dynamics of capital intensity will allow us to draw a conclusion about the success of investments in the fixed capital of the enterprise. The article contains formulas for capital intensity, as well as an example of calculation and analysis of the indicator.
Where is the capital ratio applied?
It is effective to calculate the capital intensity ratio for those companies where the production process does not directly correlate with the level of intellectual investment:
- capital construction,
- chemical industry,
- mining industry,
- ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy,
- heavy engineering, etc.
. Composition and structure of fixed production assets
Capital ratio formula
Capital intensity is calculated using the following formula:

Where FE is capital intensity,
OSav – average annual cost of fixed assets,
B – cost of gross (sold) production.
In order to have data on the cost of fixed assets at the beginning of the analyzed period (OSng), the cost of introduced (OSvved) and retired fixed assets (OSvyb) during the year. And also data on the number of months when the introduced funds were used (M1), and the withdrawn funds were not used (M2).
We obtain the following formula for calculating OCsr:

Calculation of capital intensity for products sold (in the denominator) is the most stringent indicator - it reflects the cost of fixed assets per ruble of products sold. Not all products produced will be sold, so using revenue as the basis for calculation, we have a targeted analysis tool.
Economic sense
The economic meaning of the coefficient follows from the formula. It shows how many rubles of OPF are contained in a ruble of manufactured products. The unit of measurement is rubles.
How to find capital ratio from balance sheet
Capital intensity ratio on the balance sheet = line 1150 at the beginning of the year + line 1150 at the end of the year * 0.5 / line 2110
No standard values have been established for this indicator. Companies should evaluate and analyze it over time in comparison with past periods of activity, as well as in comparison with similar organizations in the industry.
. Dynamics of capital productivity, capital intensity and other indicators

What determines the value of capital intensity?
The amount of capital intensity in a company depends on the following factors:
- The ratio of the growth rate of the average annual cost of open-end holdings and the volume of production. The more goods we produce, the lower the capital intensity ratio per unit of production.
- The level of mechanization and automation of production, modernization of existing equipment. If a new OPF is acquired, the capital intensity ratio of the enterprise will increase. This is a temporary phenomenon, since it takes some time to master the equipment and obtain technological returns.
- Increasing the operating time of machines and equipment (increasing the shift ratio).
- Improving the use of enterprise production capacity. During the period of technological equipment, it is necessary to use all possible resources from existing equipment.
- Increasing the share of the active part of fixed production assets.
- Personnel qualification level. There is a clear connection here with labor intensity and labor productivity. To do this, you need to analyze labor productivity. It is also important to motivate staff to increase productivity in the workplace. .
- Price level for products sold, etc.
Capital intensity analysis
The main rule: the higher the capital intensity indicator, the less efficiently the production capacity is used.
Successful production is characterized by an increase in output that outpaces the growth in the value of fixed assets - the capital intensity indicator should decrease (see Table 1).
Table 1. Capital intensity analysis
|
Coefficient value |
Comment |
|
The coefficient increases |
This trend indicates incomplete or irrational use of OPF. This means that some fixed assets are not fully involved in the production process. As a rule, this may be idle equipment, improper organization of working hours, unused production areas, etc. |
|
The coefficient is decreasing |
Production efficiency increases, i.e. fixed assets fully fulfill their purpose in producing products. |
|
The enterprise's capital intensity ratio exceeds the industry average ratio |
In this case, we can talk about a decrease in the efficiency of using production capacity by a particular company compared to competitors who form the industry average. |
|
The ratio is below the average capital ratio for the industry |
High efficiency of using OPF compared to competitors. This indicator allows us to consider the enterprise as a competitive player in the production market |
How to influence capital intensity
There are 2 types of strategies for using OPF:
- An intensive strategy involves updating and re-equipping the enterprise's capacities, which entails greater output.
- Extensive includes redistribution of equipment operating time, introduction of additional shifts, reduction of downtime and proper organization of labor. To reduce the capital intensity ratio, it is necessary to take care of the rational use of production space and load the equipment to work at full capacity. Increase the number of shifts in order to increase the volume of products produced.
Calculation example
The Alpha company, which carries out logging operations, has the following indicators (Table 2).
Table 2.Indicators for calculation
|
Indicator |
2017 |
2018 |
Deviation |
|
Fixed assets |
|||
|
Capital ratio |
We see that in 2017 the cost of fixed assets was 0.31 rubles for each ruble of products produced, and in 2018 – 0.33 rubles. An increase in capital intensity indicates that production capacities are not operating at full capacity, i.e. are not used rationally. The increase in capital intensity was 6%.
The industry average indicator of the capital intensity ratio in the logging industry is at the level of 0.67. Based on this, Alpha LLC can be considered as a serious competitor.
In practice, financial managers should maintain a “Report on the efficiency of use of fixed assets,” which will help track the dynamics of changes in capital intensity, detect weaknesses in the structure of fixed capital and take the necessary actions to optimize the general fund.
Conclusions
The capital intensity indicator is not so often used in the analysis of the financial and economic activities of an enterprise. However, using this indicator, it is possible to assess the success of investments in fixed capital and the utilization of production capacities in comparison with previous periods of activity. See more about the method of express business assessment.
A change in the capital intensity ratio up or down signals production efficiency. Assessing its dynamics allows you to develop the right strategic decision: increase the number of shifts in order to increase the volume of output, reduce downtime, or change the organization of work with an increase in productivity.
Capital productivity and capital intensity - the formulas for these indicators have an inverse relationship. The value of capital productivity shows how effectively an enterprise uses the fixed production assets at its disposal. Capital intensity reflects the value expression of fixed assets per unit of output. A one-time calculation of this analytical parameter does not make it possible to objectively assess the effectiveness of the involvement of fixed assets in the production process, therefore, monitoring the indicator over time is required.
When the capital intensity of products is calculated, the formula reflects the level of costs. The lower the result, the higher the final profitability of the main activity. When tracking the dynamics of changes in this indicator, it is necessary to strive for negative growth. If capital intensity increases and capital productivity decreases, the production potential of a business entity is either not fully used, or the operation of fixed assets is carried out irrationally.
The specificity of capital intensity is that it must be calculated separately for each type of product or line of activity. The parameter can be displayed for several types of assets:
Capital intensity of gross output - the formula is aimed at analyzing the efficiency of the production process within a separate enterprise or industry. The indicator is general in nature; it is calculated using the total cost of all manufactured products.
Capital intensity of fixed assets.
Capital intensity for finished, marketable products.
Capital intensity: calculation formula
To determine the value of capital intensity, cost expressions of several indicators will be required:
level of income from core activities (revenue from sales of finished products);
the value of the fixed assets owned by the enterprise.
The last element is reflected in accounting and reporting as of different dates - at the beginning of the analyzed period and at the end date of the selected time interval. For calculations, the average for the year is used. Revenue is equal to the accumulated amount of income over a similar period of time.
Capital intensity of fixed assets – formula:
Average annual cost of fixed assets, rub. / Revenue, rub.
The average annual valuation of property assets is derived by adding the sum of the value of fixed assets at the beginning of the year and at the end of the period, followed by dividing the total by 2. If there is a calculated capital productivity indicator (it is determined by dividing the amount of annual revenue by the average annual cost of fixed assets), you can use it in calculations. In this case, the capital intensity will be equal to:
1 / Capital productivity
To calculate capital intensity, the formula for the balance sheet uses data from Form 1 and Form 2 of the accounting (financial) statements:
Value of line 1150 “Fixed assets” of form 1 / Value of line 2110 “Revenue” of form 2
When assessing the level of capital intensity based on the volume of gross output, the average valuation of fixed assets should be divided not by the revenue received, but by the cost of gross output.
When the commodity mass is used as the main guideline, instead of revenue, the indicator for the valuation of commercial products is substituted into the formula. The monetary expression of the cost of commodity products is determined by reducing the volume of gross output by assets that are in the production stage (semi-finished products and work in progress).
Capital intensity: calculation formula using an example
The initial data for calculation on line 1150 of the balance sheet are presented by the following indicators:
Revenue from line 2110 of the “Income Statement” (Form 2):
in 2016, the company earned 503 thousand rubles from the sale of its products;
in 2017, the revenue value was at the level of 504 thousand rubles;
in 2018, we managed to increase sales income to 515 thousand rubles.
How to determine capital intensity (balance sheet calculation formula):
in 2016, the calculation result is 0.39 rubles. (195 thousand rubles / 503 thousand rubles);
in 2017, capital intensity was 0.40 rubles. (203.5 thousand rubles / 504 thousand rubles);
in 2018, calculations showed that capital intensity was 0.39 rubles. (203 thousand rubles / 515 thousand rubles).
The average annual cost of fixed assets is displayed. In 2016, this figure amounted to 195 thousand rubles. ((188 thousand rubles + 202 thousand rubles) / 2), in 2017 it was equal to 203.5 thousand rubles. ((202 thousand rubles + 205 thousand rubles) / 2), in 2018 it was at the level of 203 thousand rubles. ((205 thousand rubles + 201 thousand rubles) / 2).
The capital intensity for each year is calculated:
Based on the dynamics of changes in capital intensity, it is clear that property assets are used quite efficiently. Fluctuations in the costs of fixed assets are insignificant; an increase was recorded in 2017, but the deviation was eliminated at the end of 2018.
Definition: Return on assets - This is the cost of manufactured products per 1 ruble. the cost of the enterprise's fixed production assets.
This indicator is used to determine the efficiency of using the entire set of fixed production assets of an enterprise
 cost of OPF;
cost of OPF;
FO– capital productivity;
VP– product release.
|
Base year |
Reporting year |
|
|
|
Definition
Capital intensity –……………..

FE– capital intensity;
FO– capital productivity;
|
Base year |
Reporting year |
|
|
|
Definition
Capital-labor ratio – …………………………

 average annual cost of fixed production assets;
average annual cost of fixed production assets;
FV– capital-labor ratio;
H Wed– average number of workers
We can conclude that the capital productivity indicator in the reporting year is higher than in the base year because OPF and VP are higher in the reporting year.
The capital intensity indicator in the reporting year is correspondingly less than in the base year because the capital productivity ratio is higher.
The capital-labor ratio in the reporting year is almost 2 times greater than in the base year because and the number of workers is less and the average annual cost is more in the reporting year.
2. Calculation of labor productivity
Definition: Labor productivity – …………………………………..

P r- labor productivity;
VP - product release;
H Wed- average number of employees of the enterprise.
Conclusion: Labor productivity in the reporting year was higher by 6.96 thousand rubles/person. because More products were produced in the reporting year and the number of employees at the enterprise is less than in the base year.
3. Calculation of indicators for the use of working capital
Definition: Turnover ratio –

TO about
VP– product release;
OS– balance of working capital.
|
Base year |
Reporting year |
|
|
|
Definition: Average turnover period – ….
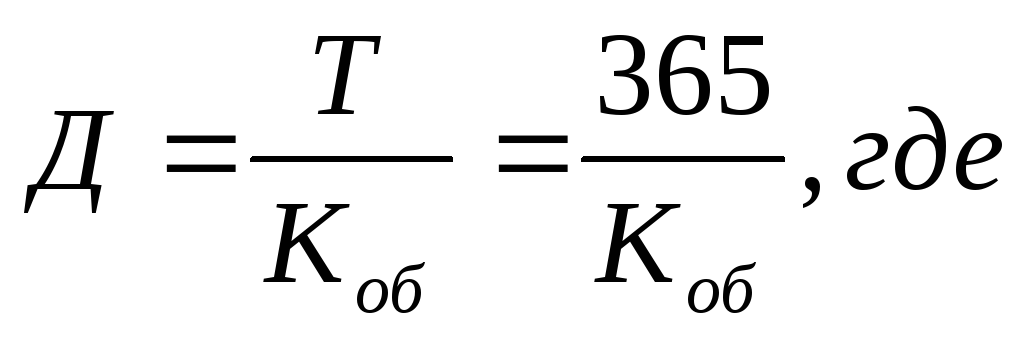
D– average turnover period;
T– number of days in a year;
TO about- turnover ratio.
|
Base year |
Reporting year |
|
|
|
Definition: Working capital utilization factor –……..
…………………………………………………………………………………………

TO about- turnover ratio;
TO h- working capital load factor.
|
Base year |
Reporting year |
|
|
|
Conclusion: When determining the working capital load factor, it is clear that in the base year it is higher, because turnover ratio is lower.
4. Calculation of the cost of production and its share in the cost of products sold
Definition: Product cost –…………………..
 ----
----

P- profit from sales of products;
IN– revenue from product sales;
WITH- cost of production.
|
Base year |
Reporting year |
|
C = 225-55=170 (thousand rubles) |
C = 275-75=200 (thousand rubles) |

specific weight– share of cost of goods sold;
WITH- cost of production;
VP– product release.
|
Base year |
Reporting year |
|
|
|
When determining the cost and share, it is clear that the cost in the base year is 30 thousand rubles less, and the share of the cost of products sold is approximately 3% more.
DEFINITION
The capital intensity indicator is financial ratio. It is inversely related to the capital productivity indicator. The capital intensity formula on the balance sheet characterizes the cost of fixed assets of production per each ruble of manufactured products.
The capital intensity indicator is measured in rubles, and its calculation requires data from the enterprise’s financial statements.
The basic formula for capital intensity is as follows:
F=OSsg/V
where Ф is capital intensity in rubles,
OSsg – average annual cost of fixed assets (rub.),
B – the amount of revenue from product sales (rub.).
The capital intensity indicator is the inverse indicator of capital productivity, so it can be calculated using another formula:
Capital intensity = 1/Capital productivity
The average annual cost of fixed assets is determined by the following formula:
OSsg = (OSng + OS kg) / 2
Here OSsg is the average annual cost of fixed assets (funds),
OS ng and OS kg are the corresponding indicators of fixed assets at the beginning and end of the year.
Revenue from the sale of sold products is determined by multiplying the price of the product by its quantity:
B = C * K
Formula for capital intensity on balance sheet
The formula for capital intensity on the balance sheet uses the cost of fixed assets (initial and residual value).
Formula for capital intensity on balance sheet:
Ф = line 1150/ line 2110
Here Ф is capital intensity (rub.),
Line 1150 from the balance sheet (cost of fixed assets),
Page 2110 from the income statement (revenue from sales of products).
Standard for capital intensity indicator
The formula for capital intensity on the balance sheet shows the value of fixed assets, which is part of each ruble of manufactured products. However, there is no single standard value for the capital intensity indicator.
If we consider the indicator in dynamics, then the smaller its value becomes, the more efficient the degree of equipment utilization. A favorable sign for any company is a tendency towards negative dynamics of the capital intensity indicator. If the capital intensity increases, and the capital productivity indicator falls accordingly, then we can talk about the following fates:
- The production capacity of the enterprise is used irrationally,
- The need to search for additional sources of reserve, etc.
Different economic sectors will have specific results when calculating the capital intensity formula on the balance sheet. For this reason, the analysis of the capital intensity ratio is carried out either for a similar industry or for the same type of product.
Types of capital intensity
Capital intensity can be of several types depending on the participation of fixed assets in the production process:
- Full(used to justify the rate and proportion of growth in expanded reproduction, when assessing the effectiveness of the industry structure and location of production, pricing and determining the needs for fixed assets for future periods);
- Straight(taken into account in accordance with the cost of fixed assets of any production process in the value of the increase);
- Indirect(contains the value of fixed assets operating at related enterprises and indirectly participating in the production of related and component products of a particular enterprise).
Examples of problem solving
EXAMPLE 1
| Exercise | Calculate the capital intensity of the enterprise if the following accounting indicators for 2 years are given: Enterprise revenue (line 2100 of the financial results report) 1 year – 400 thousand rubles, 2nd year – 350 thousand rubles. Cost of fixed assets (line 1150 of the balance sheet): 1 year – 280 thousand rubles, 2nd year – 270 thousand rubles. |
| Solution | Formula for capital intensity on balance sheet: Ф = line 1150/ line 2110 F (1 year) = 280/400 = 0.7 rubles, F (2 year) = 270/350 = 0.77 rubles Conclusion. We see that for every ruble of goods produced, the amount of fixed assets is 70 kopecks in the first year, and 77 kopecks in the second year. The figure increased in the second year, reflecting its less efficient performance. |
| Answer | F (1 year) = 0.7 rub., F (2 year) = 0.77 rub. In the second year, the efficiency of the enterprise decreased. |
EXAMPLE 2
| Exercise | Determine capital intensity according to the balance sheet if the following indicators are given: Line 2110 (amount of revenue): 1 year – 210,500 rub., 2nd year – 190,200 rub. Line 1150 (cost of fixed assets): As of December 31 of the first year - 140,250 rubles. As of December 31 of the second year - 116,800 rubles. |
| Solution | The formula for capital intensity on the balance sheet to solve this problem: Ф = line 1150/ line 2110 F (1 year) = 140,250 /210,500 = 67 kopecks, F (2 year) = 116,800 /190,200 = 61 kopecks. Conclusion. We can conclude that to obtain an income of 1 ruble in the 1st year, capital was used for 67 kopecks, and in the second year for 61 kopecks. At the same time, the coefficient decreased, which indicates an increase in the efficiency of its work. |
| Answer | F (1 year) = 67 kopecks, F (2 year) = 61 kopecks. |







 (days)
(days) (days)
(days)


